Stellate Macrophages Are Found in the Liver and Are Responsible
Gut bacteria bacterial endotoxins and. Stellate macrophages are found in the liver and are responsible for removing bacteria and worn-out cells.
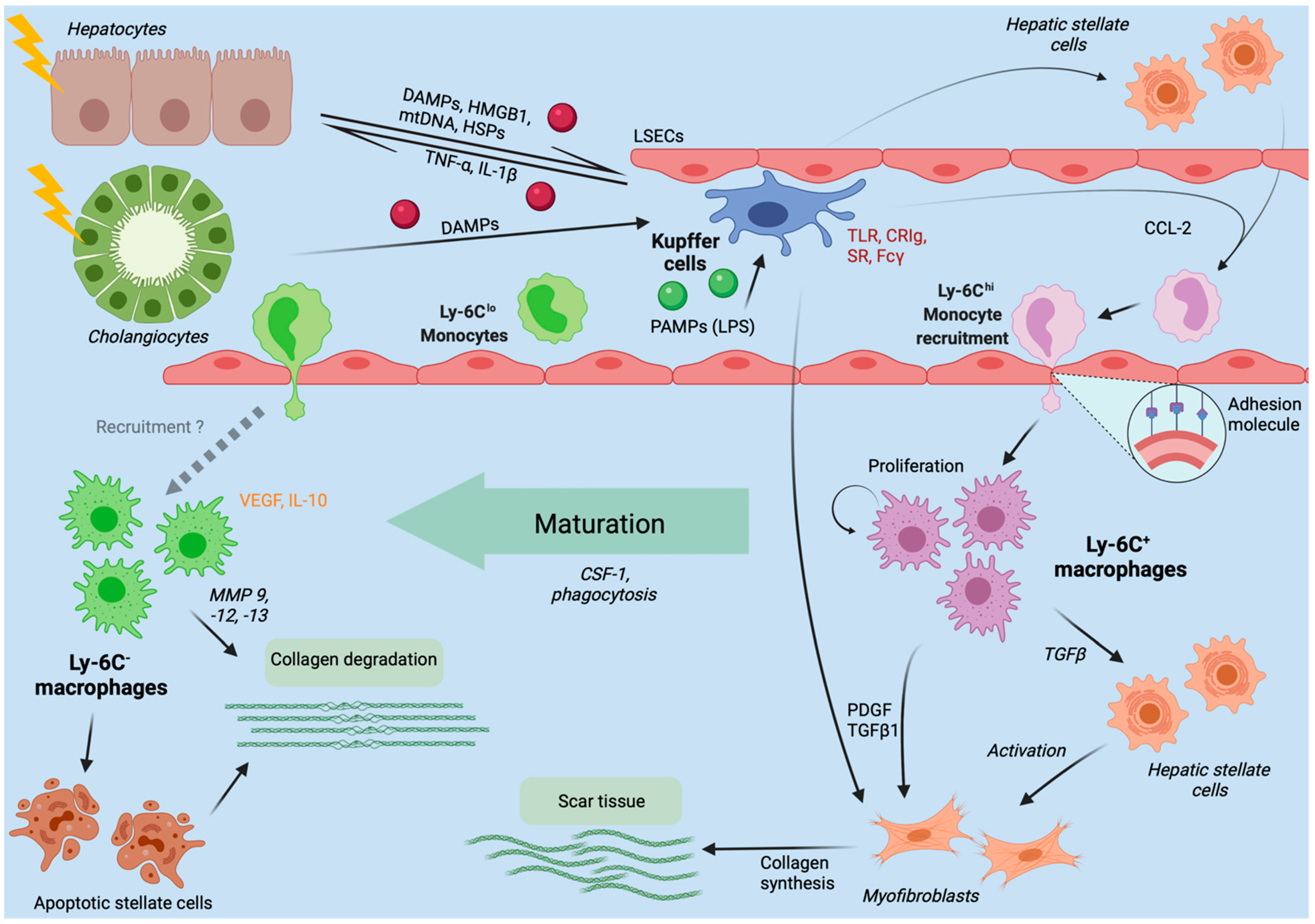
Ijms Free Full Text Liver Injury And The Macrophage Issue Molecular And Mechanistic Facts And Their Clinical Relevance Html
These specialized macrophages are specifically found in the liver.

. Kupffer cells are specialized stellate macrophages which function in the liver to remove ingested bacterial pathogens that enter from the gut to the blood. True 6 The pharyngeal-esophageal phase of swallowing is involuntary and is controlled by the swallowing center in the thalamus and lower pons. Among liver cells hepatic stellate cells HSCs and macrophages play critical roles in fibrosis and HCC.
Stellate cells are GABAergic inhibitory interneurons whose somata are located in the molecular layer. They are a component of the host immune system and are involved in the metabolism of various compounds. This study shows that the Kupffer cell niche is composed of stellate cells hepatocytes and endothelial cells that together imprint the liver-specific macrophage identity.
Macrophages have two main functions. Hepatic stellate cells also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver also known as the space of Disse. Also known as Kupffer-Browicz cells or stellate macrophages.
Although phagocytic function of macrophages was not systematically studied in human liver disease isolated reports have found evidence of impaired macrophage phagocytosis in cirrhotic patients. They are first a factory of protein synthesis and secondly they are garbage trucks. Relaxin is an antifibrotic peptide hormone previously assumed to directly reverse the activation of hepatic stellate cells for liver fibrosis resolution.
Macrophages were responsible for. Nevertheless the mechanisms through which aHSCs regulate macrophages phenotype and function during liver fibrosis and cirrhosis remain unclear. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body.
Trating hepatic macrophages HM and the regenera-tion of functional parenchyma23 Hepatic stellate cells HSCs are considered the main fibrogenic cell type in the liver and are responsible for the production of vari-ous types of extracellular matrix23 HSCs undergo a well-characterized activation process during which. In fact Kupffer cells make up 80 to 90 of all the macrophages in the entire human body. Liver Kupffer cell LXRa Nr1h3 Id3 stellate cell endothelial cell niche macrophage fibroblast Notch Bmp9 monocyte.
This study has demonstrated for the first time in humans a correlation between hepatic iron concentration and stellate cell activation in haemochromatosis which is reversed by iron removal. As major innate cells in the liver macrophages have inducible plasticity. True The thirst center in the brain is located in the hypothalamus.
As identified in the early 1970s the specialized function of Kupffer cells is mainly due to their peroxidase activity. The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis which is the formation of. Stellate macrophages are found in the liver and are responsible for removing bacteria and worn-out cells.
Humoral factors from either iron-loaded hepatocytes or activated Kupffer cells may be responsible for early s. Kupffer cells also known as stellate macrophages and KupfferBrowicz cells are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. 5 Stellate macrophages are found in the liver and are responsible for removing bacteria and worn-out cells.
Question 25 Stellate macrophages that are found in the lives are responsible for removing bacteria and wom-out unable to perform duty cells. Activated hepatic stellate cells aHSCs regulate the function of immune cells during liver fibrosis. This kupffer-browicz cells are specialized cells present in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids.
These two cell types interplay and remodel the ECM and immune microenvironment in the. This is the key difference between Kupffer cells and Hepatocytes. A stellate shaped cells lining in the liver sinusoids are known as kupffer cells.
Are stellate cells interneurons. 5 Stellate macrophages are found in the liver and are responsible for removing bacteria and worn-out cells. 25 TRUE stellate macrophages that are found in liver responsible for removing bacteria and worm out cells Because of presence of HCL 26 TRUE The circular f View the full answer Transcribed image text.
So these cells are also known as stellate macrophages. Hepatocytes are the majority of the liver cells which make up about 80 of the cells in the liver and they secrete bile. These cells are adhesive to their endothelial cells made up of blood vessel walls.
6 The pharyngeal-esophageal phase of swallowing is involuntary and is controlled by the swallowing center in the thalamus and lower pons. In fact Kupffer cells make up 80 to 90 of all the macrophages in the entire human body. Kupffer cells also known as stellate macrophages and KupfferBrowicz cells are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls.
The liver Kupffer cells also known as stellate sinusoidal macrophages or Kupffer-Browicz cells are macrophages found in the sinusoids of the liver. Kupffer cells also known as stellate sinusoidal macrophages or Kupffer-Browicz cells are macrophages found in the sinusoids of the liver. As the name indicates they are big cells macro that eat things phage.
Macrophages of course are found throughout the body not just in the liver. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body.
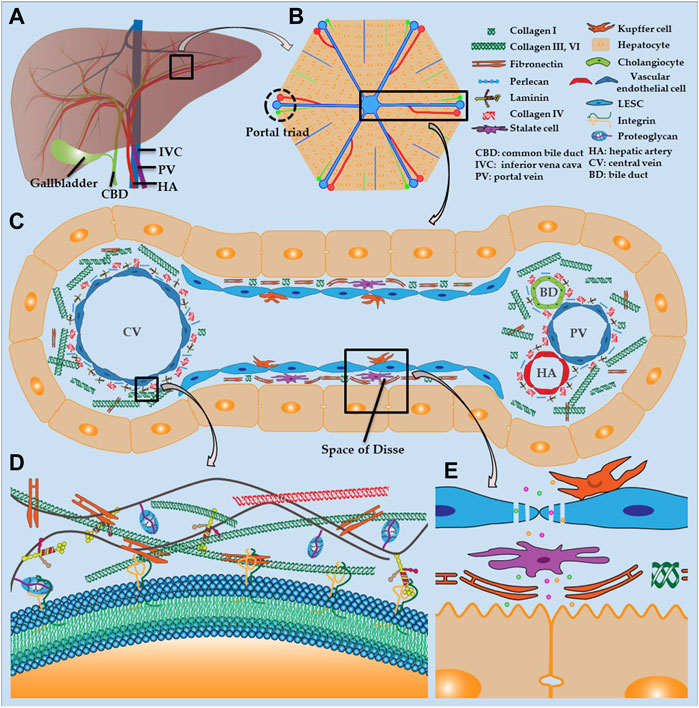
Frontiers Recent Advances In Liver Engineering With Decellularized Scaffold Bioengineering And Biotechnology

Structural And Functional Organization Of The Liver A Anatomy Of The Download Scientific Diagram

Macrophage Scavenger Receptor 1 Mediates Lipid Induced Inflammation In Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Journal Of Hepatology
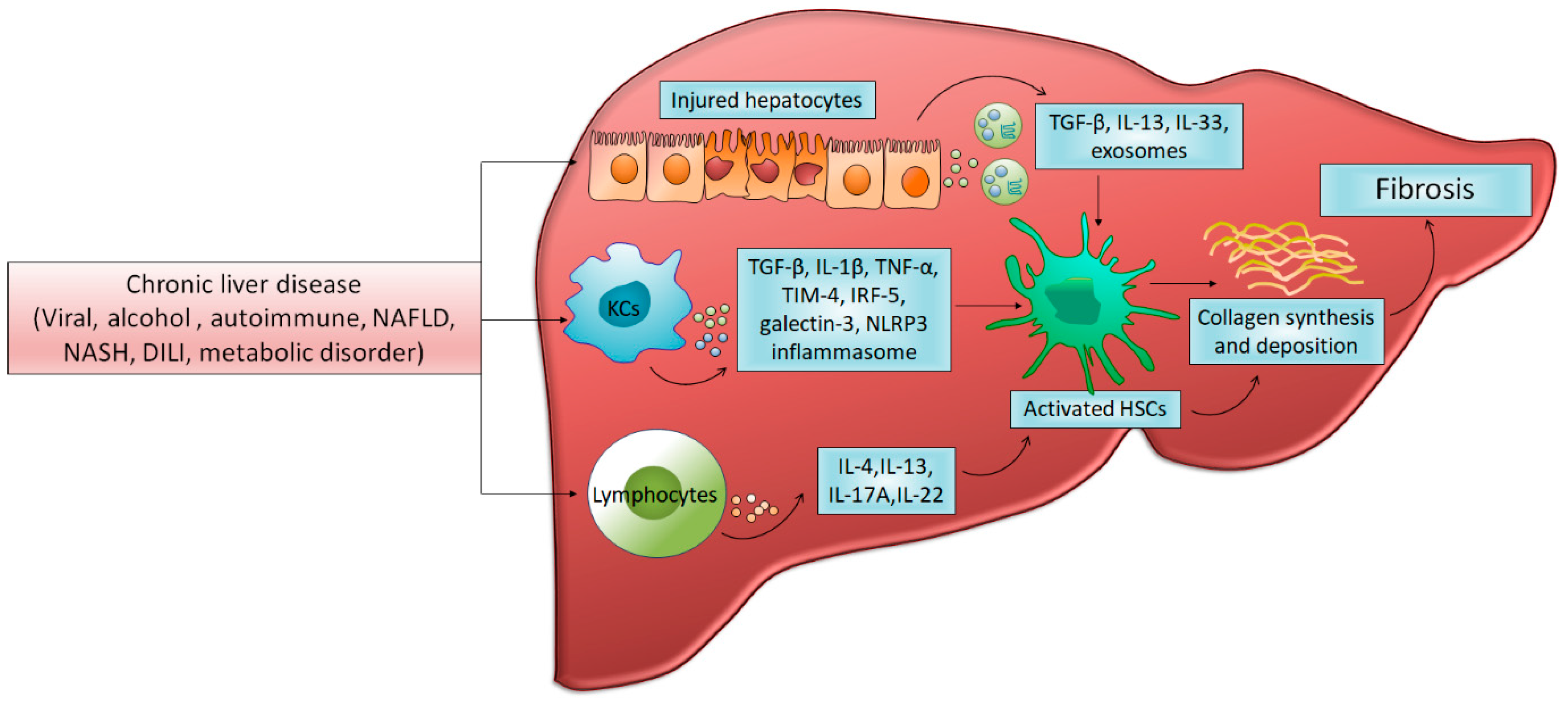
Cells Free Full Text Pathophysiology And Treatment Options For Hepatic Fibrosis Can It Be Completely Cured Html

Liver Stromal Cells Restrict Macrophage Maturation And Stromal Il 6 Limits The Differentiation Of Cirrhosis Linked Macrophages Journal Of Hepatology

The Liver As An Immunological Organ Because Of Its Distinctive Download Scientific Diagram
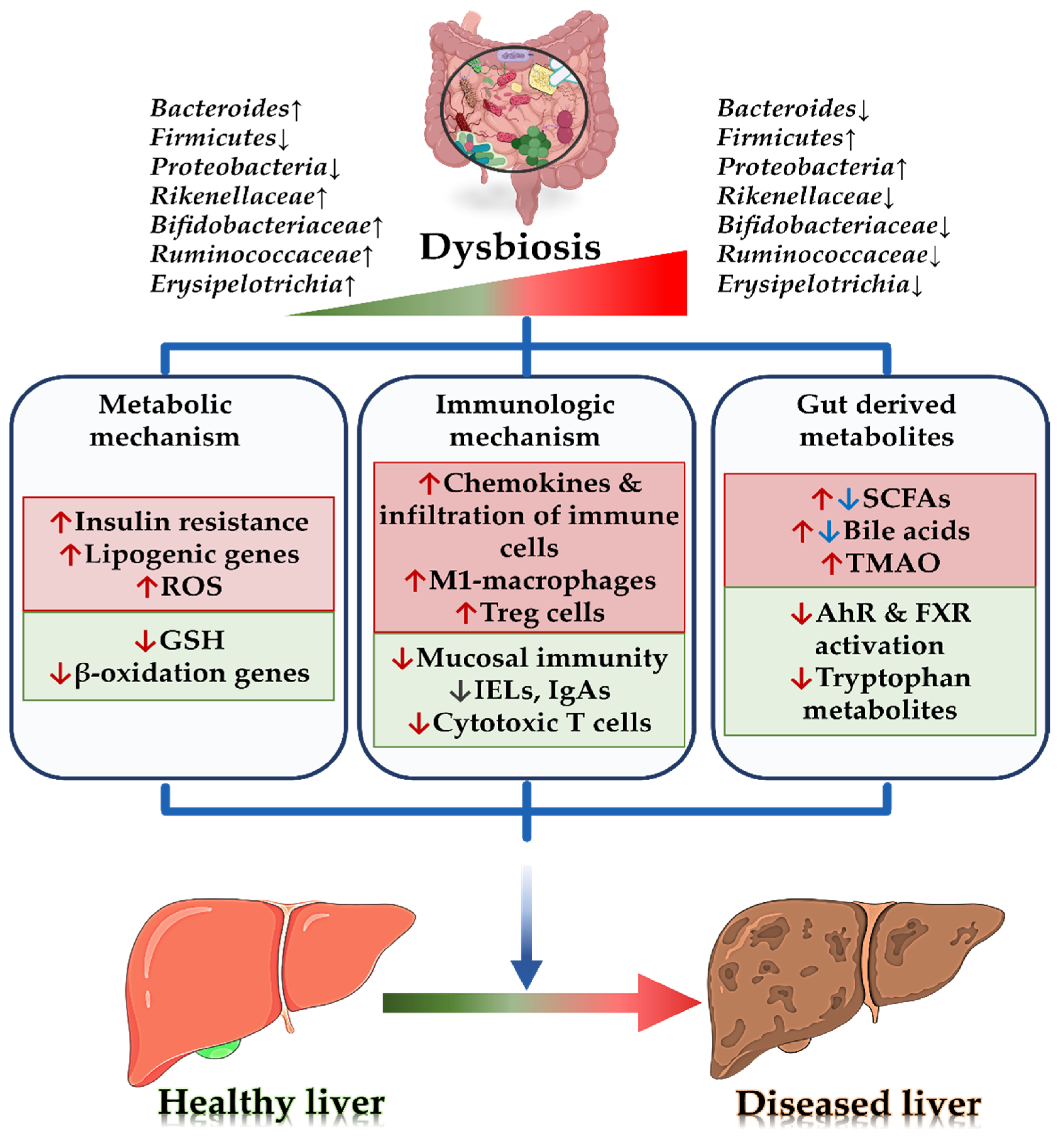
Biomedicines Free Full Text Gut Microbiome In Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease From Mechanisms To Therapeutic Role Html

Integrin B1 Enriched Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Monocyte Adhesion And Promote Liver Inflammation In Murine Nash Journal Of Hepatology

Liver And Hepatocellular Architecture A Organization Of The Hepatic Download Scientific Diagram
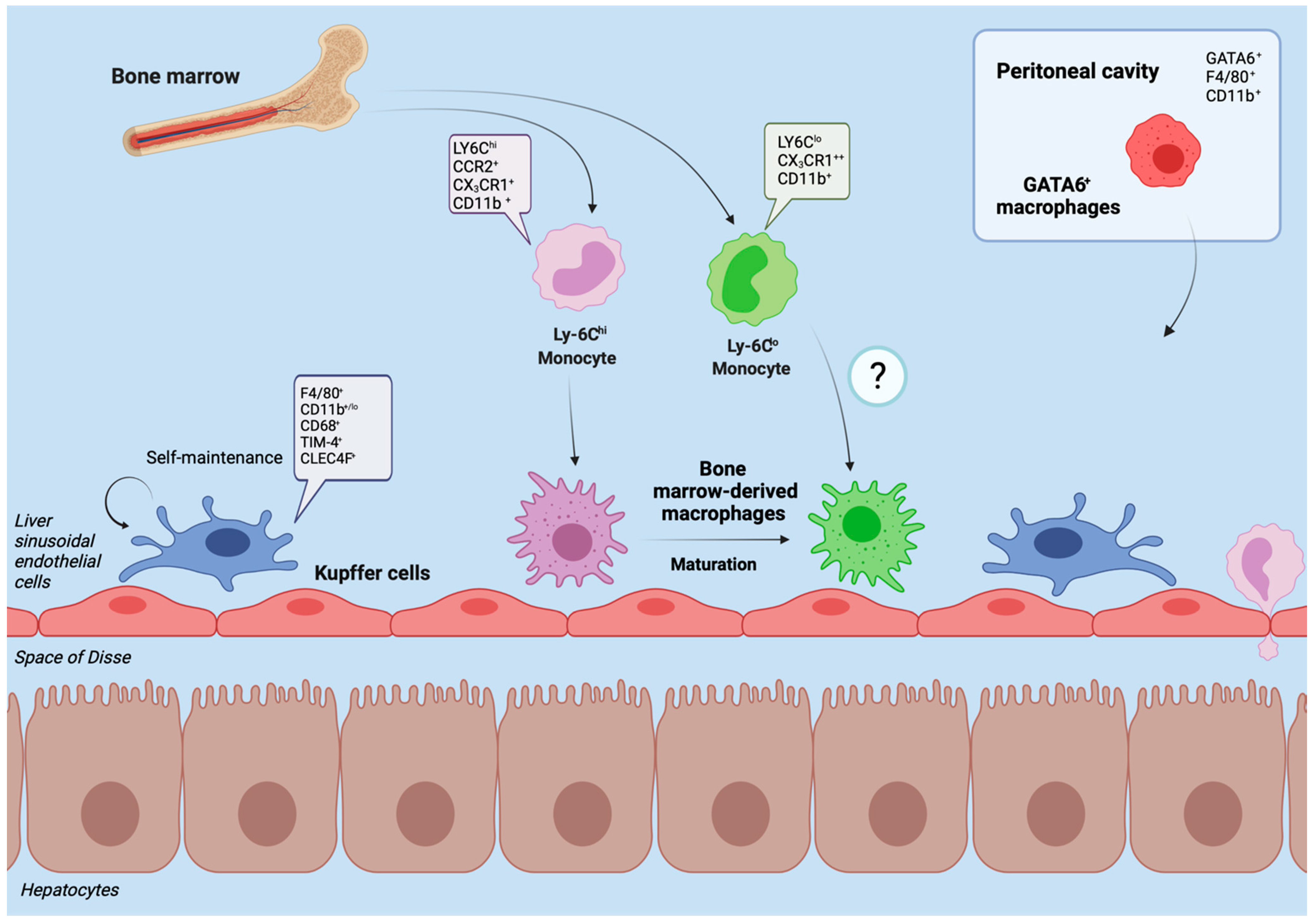
Ijms Free Full Text Liver Injury And The Macrophage Issue Molecular And Mechanistic Facts And Their Clinical Relevance Html

Advanced Preclinical Models For Evaluation Of Drug Induced Liver Injury Consensus Statement By The European Drug Induced Liver Injury Network Pro Euro Dili Net Journal Of Hepatology
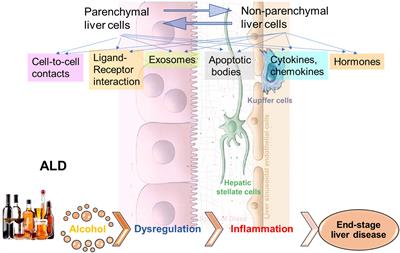
Frontiers Cell To Cell Communications In Alcohol Associated Liver Disease Physiology
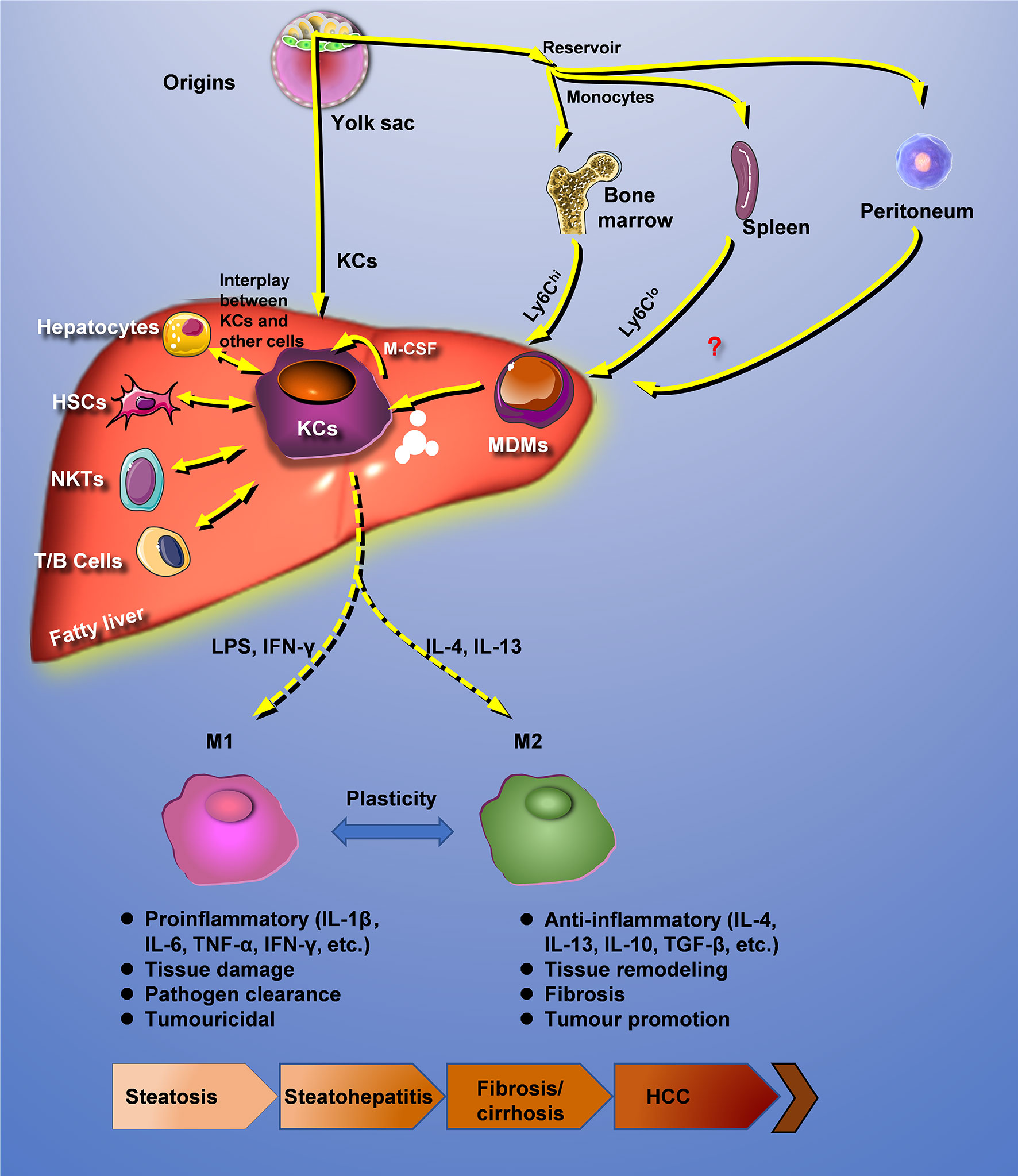
Frontiers Hepatic Macrophage As A Key Player In Fatty Liver Disease Immunology

Periodontitis Chronic Liver Diseases And The Emerging Oral Gut Liver Axis Albuquerque Souza Periodontology 2000 Wiley Online Library

Pdf Liver Injury And The Macrophage Issue Molecular And Mechanistic Facts And Their Clinical Relevance
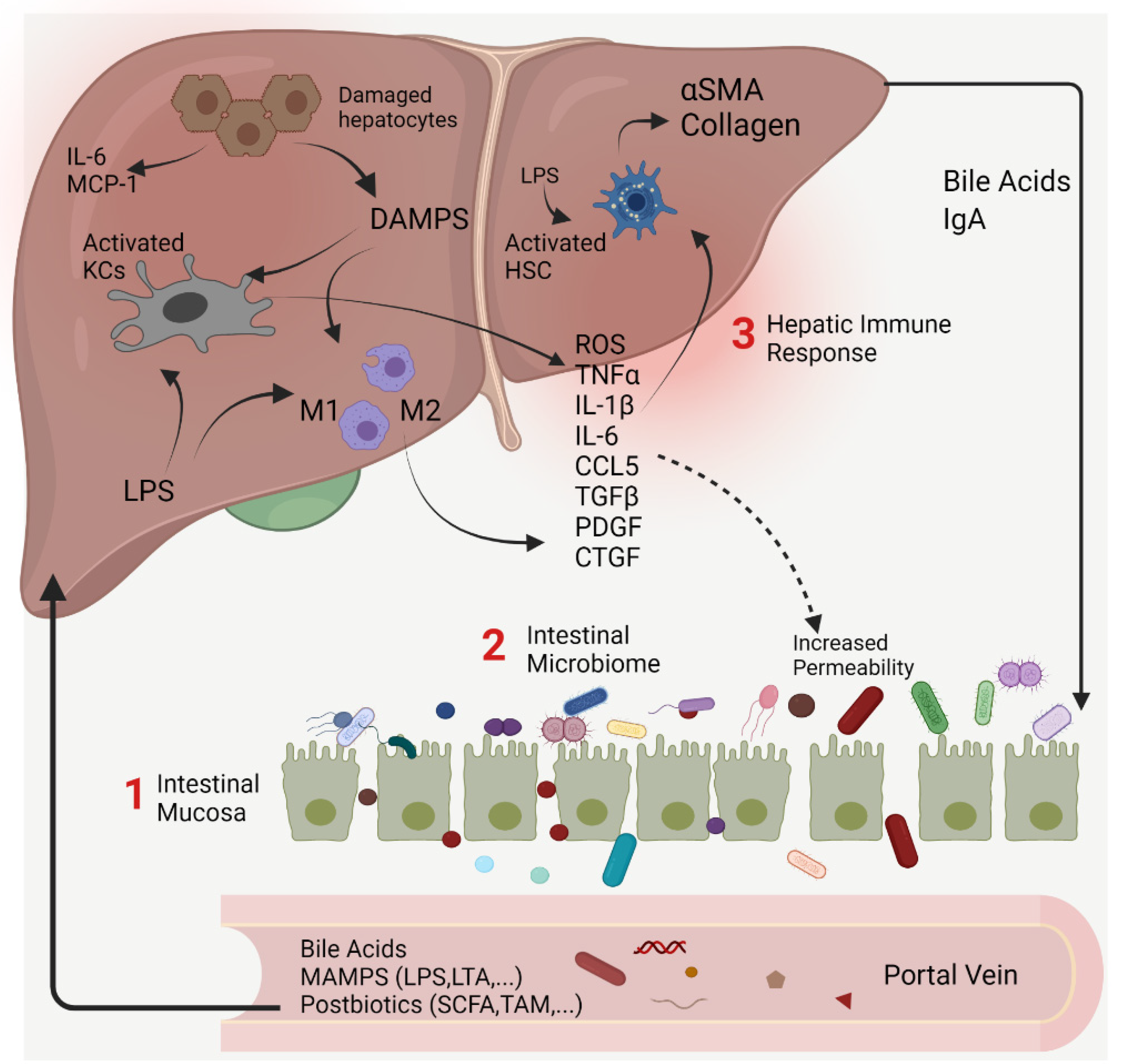
Livers Free Full Text Targeting Gut Liver Axis For Treatment Of Liver Fibrosis And Portal Hypertension Html
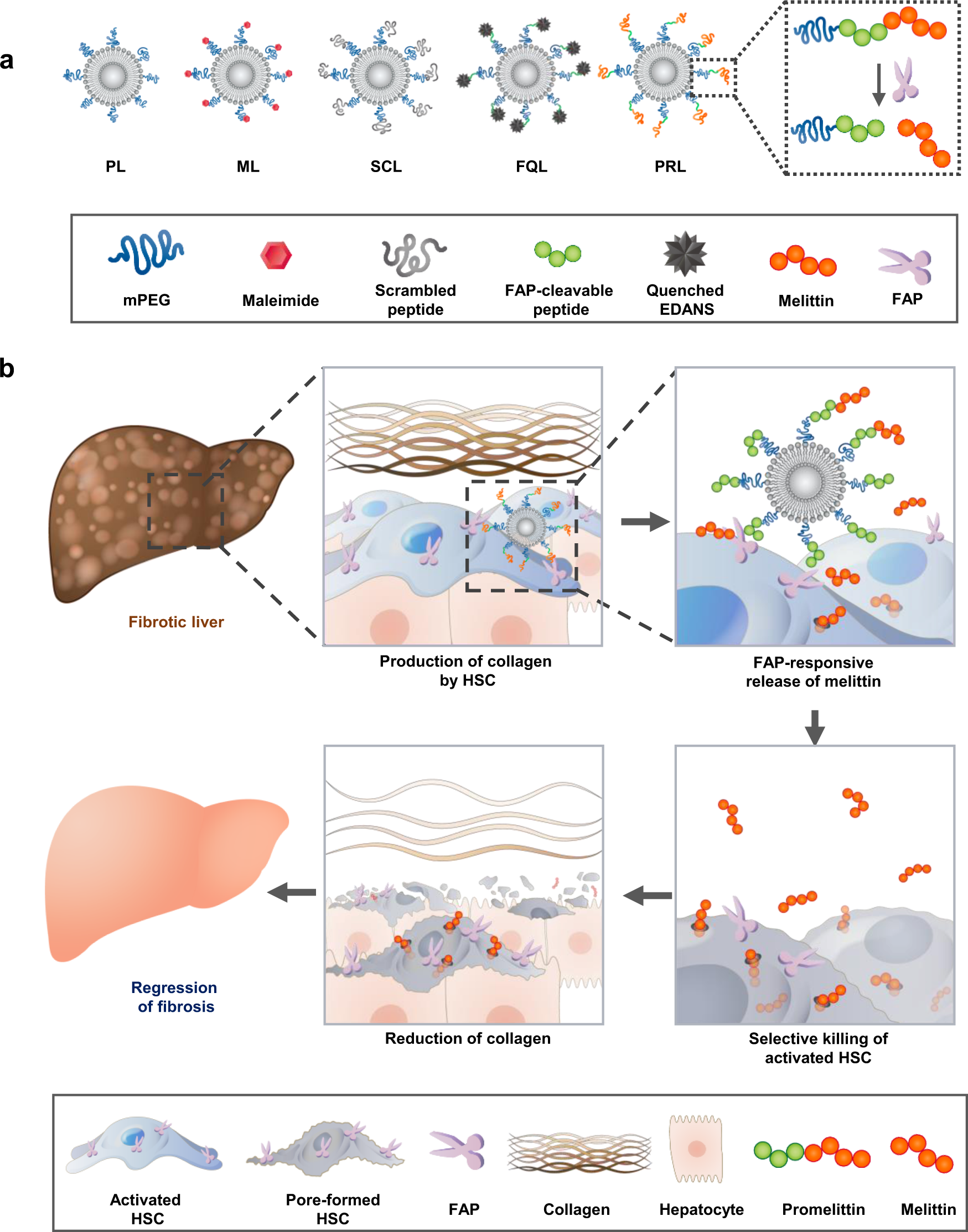
Fibroblast Activation Protein Activated Antifibrotic Peptide Delivery Attenuates Fibrosis In Mouse Models Of Liver Fibrosis Nature Communications

Liver Architecture And Evs Interactions Between Different Liver Cell Types Download Scientific Diagram

Upon Request A Look Into The Liver Medical School Studying Medicine Notes Medical Studies
Comments
Post a Comment